Waterfront Defined

Terminology
These local definitions will not only to help you know the lingo when it comes to waterfront speak, but to give you quick access tools to research waterfront to your heart’s content. Here is a quick resource to commonly used terms related to waterfront real property:
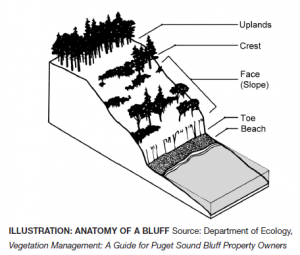
Bluff Most beaches on Puget Sound are backed by bluffs. These bluffs can vary from spectacular, high eroding cliffs to low, vegetated banks. The erosion of bluffs is a significant source of sediment on many Puget Sound beaches. One way of classifying bluffs is by the amount of sediment they provide to local beaches as they erode. This is based on how fast they erode, how high they are, and how much sand and gravel they contain. In these maps, bluffs are assigned to the following categories: Exceptional Feeder Bluffs; Feeder Bluffs; Feeder Bluff – talus; and Transport Zones. This Department of Ecology Feeder Bluffs and Coastal Landforms Map is a great tool for identifying bluff categories.
Boathouse A building designed for the storage of boats or watercraft to provide protection from the elements. The building of boathouses is generally prohibited under current environment regulations, but many grandfathered boathouses remain throughout the region.
Bulkhead A solid or open pile wall of rock, concrete, steel or timber or other materials or a combination of these materials erected generally parallel to and near the ordinary high water mark for the purpose of protecting adjacent wetlands and uplands from waves or currents.
Dock A raised walkway over water, often supported by widely spread pilings or pillars. Recent dock requirements encourage the use of decking structures and systems that encourage light and air flow to the water below. Also referred to as a pier.
Dock inspection A structural and functional evaluation by an individual or company who specializes in dock construction and repair. This can involve an underwater dive evaluation when portions of the supporting structure is in question or unobservable from above.
High bank waterfront Land that sits substantially above the natural water line, making the waterfront inaccessible without stairs or other structures, if at all.
Low bank waterfront Land that sits just above the natural water line, often delineated with a bulkhead protecting the shoreline. Low and no bank waterfront abutting a navigable lake is often considered the most desirable waterfront in the Puget Sound region.
Medium bank waterfront The most subjective of terms, this represents moderate bank land that is lower than high bank and higher than low bank waterfront.
Moorage A place where a boat or ship are secured in the water. As it pertains to waterfront real estate, this is typically on a privately owned dock or boathouse.
Navigable water “Navigability or navigable” means that a body of water is capable or susceptible of having been or being used for the transport of useful commerce. The state of Washington considers all bodies of water meandered by government surveyors as navigable unless otherwise declared by a court. See Who Owns the Water?
No bank waterfront Land that graduates out to the natural water line without a bulkhead separating it from the shoreline. Often described as rolling waterfront, its spacious feel at lakeside is highly desirable.
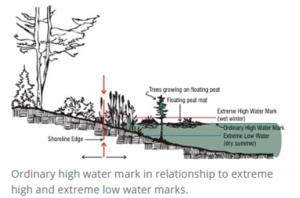
Ordinary High Water “Ordinary high water” means, for the purpose of asserting state ownership, the line of permanent upland vegetation along the shores of nontidal navigable waters. In the absence of vegetation, it is the line of mean high water.
Pier A raised walkway over water, often supported by widely spread pilings or pillars. Recent dock requirements encourage the use of decking structures and systems that encourage light and air flow to the water below. Also referred to as a dock.
Private Waterfront Land abutting the water owned exclusively by an individual land parcel. Greater waterfront footage and amenities (beach/dock/moorage) create a more valuable parcel than one with limited waterfront footage or amenities.
Shared Waterfront Land abutting the water owned in common (deeded) by owners of other often adjoining, land parcels. Fewer owner shares and deeded amenities (dock access/moorage) create a more valuable shared waterfront parcel than one with many owners or fewer amenities.
Shorelands Land which is alternately covered and left dry by the rising and falling of the water level of a lake, river, or tidal area.
“First class shorelands” means the shores of a navigable lake or river belonging to the state not subject to tidal flow, lying between the line of ordinary high water and the line of navigability, or the inner harbor line where established and within or in front of the corporate limits of any city, or within two miles thereof upon either side (RCW 79.105.060(3)). These boundary descriptions represent the general rule; however exceptions do exist. To determine if the shorelands are within two miles of the corporate limits of a city, the distance is measured along the shoreline from the intersection of the corporate limit with the shoreline.
“Second class shorelands” means the shores of a navigable lake or river belonging to the state, not subject to tidal flow, lying between the line of ordinary high water and the line of navigability, and more than two miles from the corporate limits of any city (RCW 79.105.060(17)). These boundary definitions represent the general rule; however, exceptions do exist. To determine if shorelands are more than two miles from the corporate limits of a city, the distance is measured along the shoreline from the intersection of the corporate limit with the shoreline.
(Public) Tidelands Land belonging to and held in public trust by the state for the citizens of the state, which are not devoted to or reserved for a particular use by law. Typically, the portion of land below the ordinary high water mark and the navigable water. Tide lines have been an area of great controversy in Washington State. Considered public domain through the Public Trust Doctrine. The Public Trust Doctrine does not allow the public to trespass over privately-owned uplands to access the tidelands. It does, however, protect public use of navigable water bodies below the ordinary high water mark.
“First class tidelands” means the shores of navigable tidal waters belonging to the state lying within or in front of the corporate limits of any city, or within one mile thereof upon either side and between the line of ordinary high tide and the inner harbor line; and within two miles of the corporate limits on either side and between the line of ordinary high tide and the line of extreme low tide (RCW 79.105.060(4)). In general, the line of ordinary high tide is the landward boundary. The line of extreme low tide, or the inner harbor line where established, is the waterward boundary. To determine if the tidelands are within two miles of the corporate limits of a city, the distance is measured along the shoreline from the intersection of the corporate limit with the shoreline.
“Second class tidelands” means the shores of navigable tidal waters belonging to the state, lying outside of and more than two miles from the corporate limits of any city and between the line of ordinary high tide and the line of extreme low tide (RCW 79.105.060(18)). In general, the line of ordinary high tide is the landward boundary. The line of extreme low tide is the waterward boundary. To determine if the tidelands are more than two miles from the corporate limits of a city, the distance is measured along the shoreline from the intersection of the corporate limit with the shoreline. Excerpt from the Department of Ecology Public Trust Doctrine.
Waterfront Footage The linear feet that span the water’s edge of a land parcel.
Watershed A watershed is the land area draining to a nearby river or lake, or sound.
Maps
There are many local map portals to assist in identifying topography, water conditions, hazards, and critical areas.
iMap Parcel Lookup Instructions (PDF)
Washington DNR Natural Hazards Geological Maps
Washington Geographic Information Portal Map
Department of Ecology Feeder Bluffs and Coastal Landforms Map
Department of Ecology Wetlands Inventory Map
NOAA Puget Sound Water Depth Chart
Resources
King County
King County currently has about 1200 documented residential docks and 58 private boat ramps (see shoreline land use facts). A permit is required to build, modify, alter the land abutting a shoreline.
King County Shoreline Management Fact Sheets and Links
King County Shoreline Permit Submittal Requirements (PDF)
King County Bulkhead Shoreline Requirements (PDF)
Shoreline Site Plan Requirements (PDF)
King County Shoreline Property Owner Resources
King County Lake Services and Information
Puget Sound Shoreline Stewardship Guidebook
King County Water and Shorelines Glossary
Washington State
Washington State (RCW) Aquatic Land legal definitions
DFW – Your Marine Waterfront (PDF)
DNR – Puget Sound and Coastal Geology
DNR – Puget Lowland Geological Province
Dept of Ecology – Mapping Bluffs and Beaches of Puget Sound (PDF)
WSU Guide for Shoreline Living (PDF)
UW Puget Sound Fact Book (PDF)
Environmental Protection Agency
Shoreline and Wetland Tools and Resources
King County watershed overview map
Cedar River – Lake Washington Watershed (Lake Washington waterfront properties)
Central Puget Sound Watershed (North/West Seattle waterfront on Puget Sound)
Green-Duwamish River Watershed (South Seattle waterfront properties on Puget Sound)
Sammamish Watershed (Lake Sammamish waterfront properties)
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
ERMA visualization map of Puget Sound
Bluffs, landforms and habitat classifications
The Watershed Company (site evaluation contractor) Articles
A home buyer’s guide to property with critical areas
Shoreline planning and permitting
We hope this provides an outstanding starting point in your waterfront journey. In addition to this specific research, don’t forget to evaluate all the typical aspects of your potential new home and neighborhood. We’ve compiled links to research tools from schools and geological hazards to market reports and census data.
While you’re there, you can also look up neighborhood info, including crime reporting, local government resources, parks and recreation, and school boundaries.
Of course, nothing tops having an experienced broker to guide you through the process. They’ve seen hundreds upon hundreds of homes and can help you identify the solid finds from the duds with gorgeous looking veneer.
Choosing the right broker can save you thousands on your home purchase. Whether through local market knowledge and pricing analysis allowing you to make a smarter offer, recommendations and resources to thoroughly conduct your due diligence and avoid costly mistakes, or savvy contract negotiation to help you get the terms you need, having a Windermere broker on your side is one advantage you can’t afford to sacrifice.
Find a Home | Sell Your Home | Property Research | Neighborhoods | Market Reports | Our Team
We earn the trust and loyalty of our brokers and clients by doing real estate exceptionally well. The leader in our market, we deliver client-focused service in an authentic, collaborative and transparent manner and with the unmatched knowledge and expertise that comes from decades of experience.
© Copyright 2020 Windermere Mercer Island.
The Right Timing Can Bring You Thousands More When You Sell

Ever notice how one home on your street sells well above asking price with a line of buyers out the door and an identical home comes on a month later and sits on the market for two weeks before finally selling at a reduced price? Every. Day. Counts.
It’s not always about the house. It’s also about timing the market well. In a world where potential buyers know how long you’ve been on the market down to the minute, being on the market a nanosecond longer than expected can be painful for any seller, financially and otherwise. Statistically, at mainstream price points, prices seem to peak around Day 7 and begin to slide downhill after Day 10.
How to time the market in a nutshell.
Avoid coming to market during major holiday weeks. Potential buyers take vacation too—and the fewer buyers out there looking in those precious early days, the lower the likelihood you’ll sell in the first 10 days. Look to come on the market a few days after typical vacations are over to allow buyers to re-engage in the search process. Avoid coming to market when a similar house in your neighborhood has just listed and not yet sold.
The laws of supply and demand would dictate that when supply appears abundant, demand diminishes—and the days tick on by. Even if you are by far the better house and at a better price, you might still be hurt by the curiosity around why everyone is selling now.
Avoid coming to market during bad weather or local events. Like coming on market right smack in the middle of graduation week, listing when everyone’s attention is on something other than home shopping is likely to miss the mark big time. Even if you were all set to list on a particular date, it might be better to take a deep breath and wait until the storm passes.
Do come to market when you notice an absence of great listings for sale in your price range and neighborhood. Buyers will likely feel that void too and be chomping at the bit for the next great home to come along. The chances of a perfect match between a solid buyer and a reasonable seller are best in this zone.
This is especially true if your home has challenges (outdated design, deferred maintenance, busy street, steep slope, etc.) that would make it difficult to compete with other homes out there. On the flip side of that coin, if your home is exceptional, you want to be on the market during peak season when buyers can size up your home to the competition and appreciate how much better your home is. Buyers will pay handsomely for turnkey quality when they can clearly see the difference. Come on when there is nothing else to compare to and your beautiful amenities might not see their full value potential.
The best days to come to market are Tuesday, Wednesday or Thursday. This allows for showings and open houses on evenings and throughout the weekend. If you are doing an offer review date, the best day to review offers is Monday or Tuesday. This gives buyers ample time to see your home, conduct their due diligence, complete a home inspection and sewer scope, and get their financial documentation together—all before they prepare an offer.
Final thoughts.
Look at the holiday calendar and local school district calendars to guide you toward best weeks to come to market. Don’t forget to check in big political and sporting event dates too.
Decide whether your home will shine against the competition, or be the wallflower, and adjust your timing based on real-time competition.
Of course, an outstanding listing broker can help you choose the most favorable date to bring your home to market. They analyze the market consistently and know exactly what indicators to look for. Still have questions? Contact one of our knowledgeable brokers for assistance with determining the best market timing for your home.
Find a Home | Sell Your Home | Property Research | Neighborhoods | Market Reports | Our Team
We earn the trust and loyalty of our brokers and clients by doing real estate exceptionally well. The leader in our market, we deliver client-focused service in an authentic, collaborative and transparent manner and with the unmatched knowledge and expertise that comes from decades of experience.
© Copyright 2020 Windermere Mercer Island.

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link







